GitHub for Robotics: Organizing Your First Project
2025-12-08 | By Hector Eduardo Tovar Mendoza
Are you working on a robotics project and looking for the best way to organize your code, collaborate with your team, and showcase your work to the world? If the answer is yes, then you need to know about GitHub. In this post, we'll guide you through everything you need to know to start using this powerful tool.
Why is GitHub Essential for Robotics?
In the world of robotics, collaboration and project management are key. GitHub has become an indispensable platform for robotics developers and teams for one simple reason: it centralizes the entire software development process.
From projects using ROS (Robot Operating System) to embedded systems with Arduino or ESP32, GitHub allows teams to work in a coordinated and efficient manner. A great example of this is the repository of RoBorregos, my robotics team from Tecnológico de Monterrey, where you can see how they manage their project documentation and code openly and collaboratively.
What is GitHub and Why Use It for Robotics?
GitHub is a collaborative development platform based on Git, a version control system. Think of it as "Google Docs" for your code, but much more powerful.
- Version Control: Have you ever had files like final_code.ino, final_code_v2.ino, and REALLY_final_code.ino? With Git and GitHub, you can keep a record of every change you make to your code. If something goes wrong, you can "travel back in time" and revert to a previous, working version.
- Collaboration: It allows multiple people to work on the same project simultaneously without overwriting each other's work. Each team member can work on a "branch" or a copy of the project and then merge their changes in an organized way.
- Reproducibility and Documentation: A good robotics project should be easy to understand and replicate. GitHub helps you document your work, share it with the community, and allow others to build upon what you've created.
Setting Up Your GitHub Account
Getting started is very simple.
- Create an account: Go to github.com and sign up. It's free for public repositories.
- Set up your profile: Upload a professional profile picture, add a short bio explaining your interests (mention robotics!), and a link to your LinkedIn or portfolio. A good profile makes an excellent first impression.
A great example of a GitHub profile is:
Creating Your First Repository
A repository (or "repo") is like a folder for your project. Here you will store all your code, documentation, images, and any other relevant files.
Step-by-step guide:
- In the top-right corner of GitHub, click the "+" sign and select "New repository".
- Give it a name: Choose a descriptive and easy-to-remember name. For example, arduino-robotic-arm or ros-line-follower-robot.

- Add a description: Briefly explain what your project is about.
- Initialize with a README: Check the "Add a README file" box. This file is crucial and will be the landing page for your project.
- Make it public: To allow others to see your work, make sure the repository is public.

- Click "Create repository", and you're done!
Recommended folder structure: For a robotics project, a good structure could be:
/arduino-robotic-arm
|-- /src # Source code (.ino, .cpp, .h)
|-- /docs # Documentation, diagrams
|-- /media # Images and videos of the robot in action
|-- README.md # General project description.
Adding Robotics Code and Documentation
Now it's time to upload your work.
First, you have to download git on your laptop or computer, and after installing it, open GitBash, then write:
- git config --global user.name "Your Name"
- git config --global user.email "your.email@example.com"
Uploading code
First, to make it easier to install VSCode , and then in the terminal, run the following commands
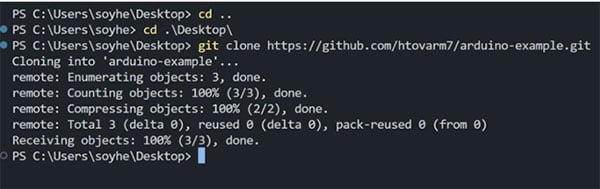
Here you go to the desktop and then clone the repo, where you can get the link from here.

Now open the folder named after the repo name.
- Writing a clear README.md: This is the most important file in your repository. Use Markdown format to structure it. A good README should include:
- A title and a description of the project.
- A list of the required hardware and software.
- Detailed instructions for compiling and running the code.
- A usage example.
- Images or GIFs of the robot in action.
An example is the following:
# arduino-example
This project is an example repository for a simple robotics project using Arduino.
## Mini Example: Line Follower Robot
This example demonstrates how to build a basic line follower robot using Arduino.
### Components
- Arduino Uno
- 2x DC Motors
- Motor Driver (L298N)
- 2x IR Sensors
- Chassis and wheels
- Battery pack
### Sample Code
``` Project Structure: arduino-robotic-arm/ ├── src/ # Source code (.ino, .cpp, .h) ├── docs/ # Documentation, diagrams ├── media/ # Images and videos of the robot in action └── README.md # General project description ```
### How it works
The robot uses two IR sensors to detect a line on the ground. Depending on the sensor readings, it adjusts the motors to follow the line.
Collaborating With a Team
The magic of GitHub lies in collaboration.
Add collaborators: In the "Settings" > "Collaborators" tab of your repository, you can invite other GitHub users to your project so they can push changes.
Branches: Instead of everyone working on the main version (main), each member can create a "branch" to develop a new feature. For example, a branch named feature/ultrasonic-sensor.
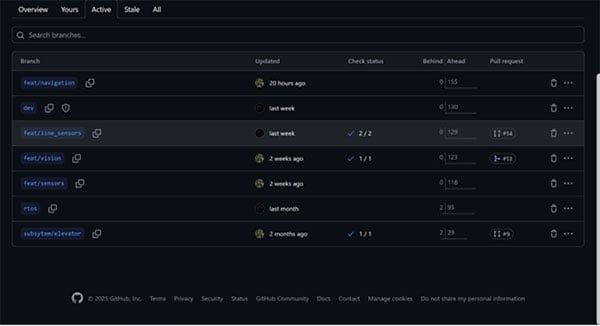
Pull Requests (PRs): When you've finished working on your branch, you create a "Pull Request" to propose merging your changes into the main branch. This allows other team members to review your code before it's integrated.

- Issues: Use the "Issues" tab to report bugs, suggest new ideas, or assign tasks to the team. It's an integrated task management system.

Showcasing Your Robotics Project
A well-organized repository is your best portfolio.
- GitHub Pages: You can create a simple and free website for your project directly from your repository. It's perfect for displaying more elaborate documentation or a gallery of your robot.
- Wiki: Every repository has a Wiki section that you can enable to create a collaborative documentation encyclopedia about your project.
- Make it appealing: Use high-quality videos, GIFs, and images in your README. A visually attractive repository invites people to take an interest in your work. For recruiters or professors, a consistent and well-documented history of "commits" demonstrates dedication and good engineering practices.
Let's recap why GitHub is the tool your robotics projects need. Throughout this guide, we've seen that it's not just a place to store code, but a complete ecosystem for development.
In summary, with GitHub, you can:
- Organize your project: Use version control to keep a flawless record of every change, eliminating the chaos of duplicate files.
- Collaborate effectively: Work with your team in a synchronized way using branches, pull requests, and issues, ensuring everyone is on the same page.
- Document and share: Create a solid foundation for your project to be reproducible, easy to understand, and valuable to the community.
- Build your professional portfolio: Turn your repository into a cover letter that showcases your technical skills to recruiters, companies, and universities.
Getting started is straightforward. I encourage you to create a repository and push your first commit to begin taking advantage of what GitHub offers.