Simple Explanation of Capacitor ESR – Why Is It Important and How Is It Specified?
DigiKey 제공
2016-09-15
Equivalent series resistance (ESR) (represented by Resr in Figure 1) describes losses associated with moving charge through a capacitor. The resistance of the electrode and lead materials is a contributing factor, and losses occurring within the dielectric material itself also occur and are often dominant. The relevance of ESR to capacitor selection is twofold: 1) it influences the AC response of the capacitor, and 2) it imposes limits on the amount of AC current that can be permitted to flow through the capacitor due to thermal limitations. Current flow through a capacitor’s ESR results in I2R losses just like any other resistor, causing a temperature increase within the capacitor that contributes to diminished device longevity.
ESR is influenced by device type and construction, and also by temperature and test frequency to varying degrees. In many cases, the ESR of a capacitor is not directly given in a datasheet, but rather communicated in terms of a summary figure such as Q, dissipation factor (DF), or Tan δ. All are quotients of a capacitor’s ESR and capacitive reactance (XC) expressed differently. Tan δ and dissipation factor are calculated as ESR/XC, and are essentially the same figure, though it should be noted that dissipation factor is usually expressed as a percentage, rather than as a simple dimensionless factor. Q is simply the reciprocal of Tan δ, or XC/ESR.
More information on the non-ideal properties of capacitors can be found here.
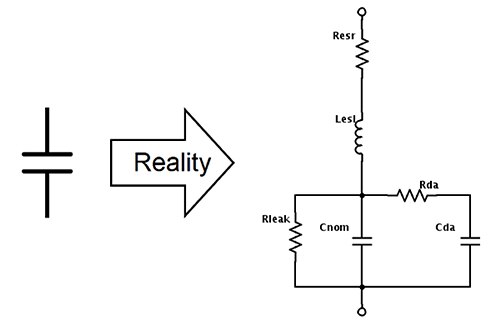
Figure 1: An ideal capacitor (left) should in reality be modeled as shown (right).

면책 조항: 이 웹 사이트에서 여러 작성자 및/또는 포럼 참가자가 명시한 의견, 생각 및 견해는 DigiKey의 의견, 생각 및 견해 또는 DigiKey의 공식 정책과 관련이 없습니다.




